October 7, 2021
5G will enable some new enterprise IoT use cases, but often means that existing 4G applications can be done at a larger scale or more efficiently. Many aspects of the 5G mobile edge can be done already with 4G LTE networks.
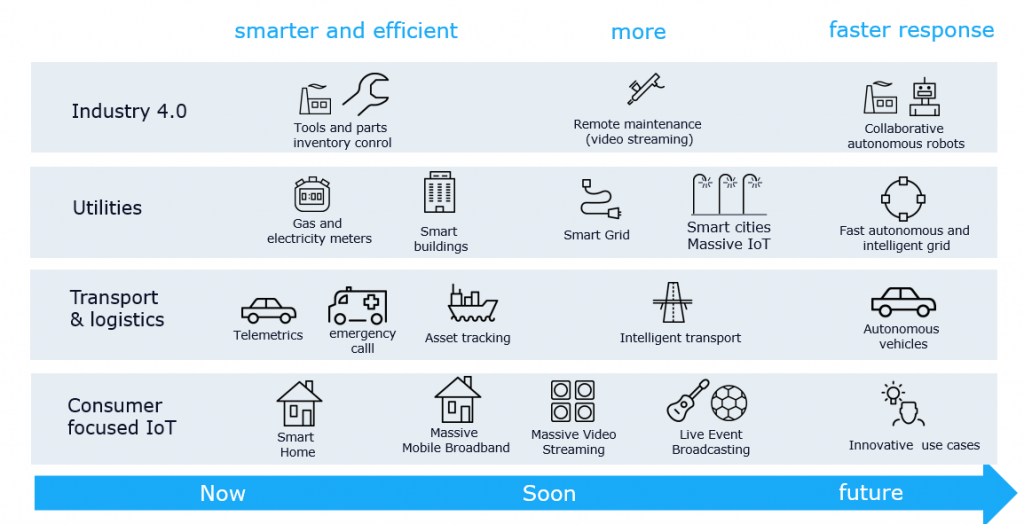
Examples for 5G consumer and business use cases in different verticals and the advantages of 5G technology
Devices with simpler hardware with a need for long battery life
The 5G Mobile IoT technologies LTE-M and NB-IoT can enable devices with simpler and more efficient hardware that need a long battery life. The longer battery life means that the devices can send information on their location for months or even years if needed:
- such as sensors in smart buildings, gas and electricity meters
- asset tracking devices, for instance, in shipping containers or tracking important post parcels
- case examples like theft protection, adding a simple mobile device that sending reports for several years without the need for a power source.
Remote working and studying
Enhanced mobile broadband will enable much more mobile data at once. Initially it will be adopted in applications that need considerably more data such as massive mobile video streaming.
During the COVID-19 lockdown we noticed that the Internet is crucial to keeping society connected. Remote working and remote studying have driven a large uptake in data usage. Remote working and studying have become the new normal for many of us. Before COVID-19 most people used connectivity for web surfing, using social media, watching a movie or video chatting with friends. Usage patterns have fundamentally changed due to remote working and remote studying. People have gotten used to interacting with many people simultaneously online. This means that connectivity is now used for multiple parallel video streams.
Remote working and studying has many benefits and we believe that massive multiple video streaming is here to stay, even after global lockdowns have been lifted ends. People will most likely continue to work and study remotely, combined with working from office and physically meeting colleagues.
During the height of COVID-19 the massive video streaming connectivity was mainly provided through WIFI and residential broadband, because people were locked down in their homes. Also, according to the Ericsson Mobile Report June 2020 mobile traffic has increased by 20 percent in some locations, especially in rural locations, during recent months. 4G technology is however not designed for massive multiple streaming. 4G works best when handling a single video stream, like watching a movie, or talking to a single person. Video chatting with many people at the same time requires 5G.
While the COVID-19 lockdowns are slowly being lifted, people will become more mobile and they will continue to consume massive mobile streams, even on the go. People have gotten more dependent on connectivity and they will demand mobile connectivity that’s even better than residential broadband. For static locations, for example working from home or in office, WIFI and residential broadband will still be the dominant mode of connectivity, but 5G will bring the ability for remote working and studying to the mobile user, so that massive video streaming can work everywhere.
The Road to 5G from an IoT Application Perspective

Remote maintenance in industrial use cases
The mobile massive video streaming will not only be relevant for the consumer market, it will also enable industrial usage scenarios such as remote maintenance. Repairing and servicing complex machinery requires expert knowledge. Before COVID-19 the people with this knowledge had to travel to these machines. This was not possible during COVID-19 which forced companies to consider remote maintenance of machinery. After this companies also realized savings on travelling cost and personal cost because remote working enables them to schedule their experts more efficiently. Experts with specialized knowledge can handle the maintenance from a central location, assisted by less trained local service personnel, robots and drones or a combination of both. This does not only add efficiencies, it reduces the risk of spreading infectious disease and is beneficial for the environment because travel is reduced. 5G enhanced mobile broadband is designed for use scenarios where people are interacting with IoT, or other people.
5G critical communication will enable IoT devices that are interacting with each other. These IoT devices and machines will need a very fast and reliable connection that 5G can provide. Companies that want to use 5G critical communication also need to consider changes to how they use the cloud. A fast response from the cloud needs a decentralized approach, with smaller local networks and cloud instances. This also improves security, since enterprises can decide to depend less on a centralized cloud and can choose instead a private cloud.
Self-driving vehicles in automotive use cases
Self-driving vehicles can benefit a lot from a faster response, reliability and improved security enabled by 5G. We believe that self-driving vehicles and robots on closed industrial locations will emerge first. Companies need to understand that for autonomous driving, 5G is just a technology. There are many other aspects such as liability and legislation on consumer privacy that need attention as well.
Cyber security challenges arising from 5G application scenarios
Any device that is connected needs security management and a secure design from the start, irrespective of the technology, from 2G to 5G from Bluetooth to WIFI.
Mobile technology like 5G offers centralized security management, whereas local networks like WIFI and Bluetooth need local security management. It is easier to apply a consistent security design in a centralized solution. Managed Mobile Connectivity is also monitored and supported by IoT experts 24/7/365, not artificial but real human intelligence by dedicated experts that can take proactive actions like disconnecting devices that behave suspiciously. In addition to human intelligence, events can be defined that trigger automatic actions when devices behave suspiciously.
This is all made possible because of the centralized operations and management of mobile IoT networks. The challenges to cyber security due to hacking applies to all connectivity technology and security by design is needed for all end points. Mobile connectivity like 5G makes it easier to implement and enforce security, compared to decentralized solutions like WIFI.