2G/3G Sunset: What It Means for IoT Connectivity
Explore what enterprises need to know about the 2G/3G sunset and how best to prepare. The end of 2G and 3G is drawing closer and it will have an impact on IoT deployments using those technologies.
With 4G and 5G being steadily deployed globally, the process of retiring 2G and 3G networks is well underway in many countries and regions. While the pace of 2G/3G sunsets is highly fragmented geographically, increasing numbers of 2G and 3G sunset dates are being published. One thing is clear: the number of shutdowns is set to increase, meaning enterprises need to take steps now to get prepared for what the future holds.
How to prepare for 2G and 3G sunsets and their impact on IoT connections
With 4G and 5G being steadily deployed globally, the process of retiring 2G and 3G networks is well underway in many countries and regions. The timing for the network shutdowns varies for each country and operator and is either decided by the local regulator, looking to free up valuable spectrum resources, or by the mobile network operator, when there is no longer enough legacy traffic to justify continued operation.
2G networks typically have been in commercial operation for more than three decades and have offered an unparalleled platform for deploying national and international high-quality IoT solutions. Many IoT solutions have long lifecycles – often of a decade or more – which means there are still large volumes of devices that are 2G only. Therefore, action needs to be taken to ensure continued operation of IoT applications as 2G and 3G networks are being sunset.
Decommissioning of 2G and 3G has been initiated and/or completed in some parts of the world, for example, in the US and Australia. Other locations have widely differing sunset dates, such as the end of 2025 for most of Europe. In the longer term, 2G and 3G networks will eventually be decommissioned everywhere so this is an issue that can’t be avoided.
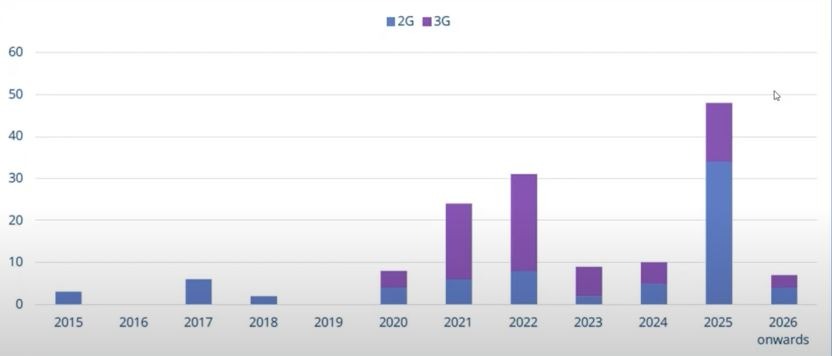
The pace of 2G/3G sunset is highly fragmented geographically and is dependent upon individual market characteristics but increasing numbers of 2G and 3G sunset dates are being published. The number of shutdowns is set to increase. GSMA Intelligence data predicts that more than 55 2G and 3G networks will be closed between 2021 and 2025 but the two technologies will not necessarily be retired at the same times and, in some markets, 2G is expected to continue in operation for a decade or more as specific services, such as mobile payments in Africa and vehicle emergency calling (eCall) in other markets, depend on 2G. In these scenarios networks are likely to continue to operate for an extended period.
On this Page:
3G shutdown – when will it take place?
3G phase out has been planned for many years and 3G networks are already shut down in several countries. Typically, these markets have universal 4G coverage and are advanced in their roll-outs of 5G so it has made sense to retire 3G and reassign spectrum to the newer technologies.
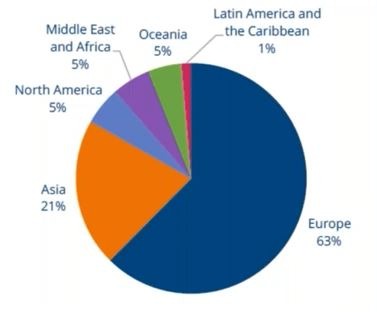
Europe has seen more sunsets in 3G than 2G so far. A total of 19 operators in 14 nations plan to switch off 3G by 2025, whereas only eight operators in eight countries are planning a 2G switch off by same time, reports GSMA Intelligence, although these numbers are growing regularly as operators reveal their plans. The 3G shutdown in Europe is well-detailed with most networks publishing their 3G sunset date. There is a new trend in Europe where some operators are extending the time, they plan to have 2G up and running. One example is in the UK where the date for sunset was set to 2025 but our latest info has seen these dates being extended because the UK government has come to an agreement with the UK mobile operators that they continue operation of their 2G networks for the coming years.
3G shutdown in the US
Again, thanks to its roll-out of 4G and 5G, the US is also well underway in 3G network shutdown, with the major operators all planning to have retired the technology by the end of 2022. In previous years, the wider Americas region has focused on the 2G radio sunset as operators have launched 5G. Operators are now utilising existing spectrum that was devoted to 2G to address the demands of 4G and 5G networks.
Sunset Strategy Guide: Adapting Connected Products for the Post-2G/3G Era
Don't Get Left Behind! Cellular Network Changes Coming
Asia’s 2G radio sunset
Service providers in Asia are retaining their 3G networks and shutting down 2G instead to re-use spectrum for 4G, which has high adoption across the region. By the end of 2025, GSMA Intelligence expects 29 operators to shut down 2G and 16 operators to close 3G with Taiwan currently the only market which has witnessed both 2G and 3G sunsets, in 2017 and 2018 respectively.
There are also a few exceptions in Asia where operators have started with the 3G sunset before the 2G sunset. An example is in Malaysia where 3G is already shut down for all operators (regulated by the government).
Another example is in Indonesia where two of three have already shut down 3G and a third has plans (currently, none of them have plans for 2G shutdown).
Africa continues to rely on 2G
In Africa, 2G markets outnumber 3G two-fold, basic feature phones still comprise 42% of all devices and end-users are incentivised to remain on them given their lower costs. In turn, this drives lower digital uptake, explaining why a negligible number of sunsets have been announced in the region.
2G and 3G shutdown - what does it mean for IoT deployments?
Many IoT applications have relied on reliable, global 2G coverage and, with long IoT device lifecycles, there are still substantial numbers of devices that are 2G only and only at mid-life in their deployments. Eventually these need to be upgraded to ensure continued operation is possible.
During the current phase, in which some 2G and 3G is being retired but other 2G and 3G networks continue to operate, IoT applications need to be able to use multiple network types to achieve sufficient coverage globally. This is complex and more costly than some IoT business cases envisaged with many structured on the basis that single-mode hardware could be used for the life of the deployment. Complete replacement or upgrading will inevitably add cost and impact on profitability so attention needs to be given to maximizing efficiency and targeting upgrades to the deployments that need them first.
This process doesn’t have to be only negative. There are also upsides to the transition to consider because moving to a new technology can enable the IoT application to take full advantage of the new network capabilities on offer and this can help soften the initial blow of having to transition. Examples include improved power consumption although with limited throughout in NB-IoT that results in longer battery life or the uplift in throughput that LTE-M offers over 2G.
Minimizing the impact of the 3G phase out on customers
With 3G already becoming a niche technology and suffering from shrinking regional and national coverage and support, it is better to act sooner than later. Once a 2G or a 3G sunset takes place it will be too late because devices that are built for 2G or 3G will become completely inoperable. This, in turn, will lead to your customers suffering and this may also happen when a service transitions to an alternative network technology. The move will involve new software and hardware and cause downtime, even in phased roll-outs so careful planning is essential to minimize impacts on customers and on the service and business reputation.
There are many examples of transitions that have not gone smoothly. One municipal transport system in San Francisco experienced a fortnight of business interruption because it relied on the 2G network beyond its sunset date, even though it had been given five years of notice of the upcoming sunset.
This highlights the complex inter-relationships in IoT between network, hardware and software and demonstrates that moving on from 2G and 3G is not always a simple upgrade path.
Telenor IoT has the long-term global experience of all the technologies involved and can help to guide you through the transition to help you optimize outcomes.
How to avoid the 2G and 3G ‘mid-life crisis’
A first step for IoT enterprises should be to review the installed base to understand what devices need to be upgraded and to create the right strategy for cost efficient transition. Next, selecting sufficiently future-proofed hardware to improve the chances of benefiting from upcoming technical innovations should be a priority. There are several alternatives to 2G and 3G that are available or soon to be offered and the relative merits of these should be carefully assessed, alongside the likely software and hardware developer ecosystem – it’s not productive to choose a technology that nobody is developing devices or apps for.
Given that the sunset problem affects a substantial number of currently operating devices, steps should be taken to prevent similar situations arising in the future. It makes little sense to migrate from 2G to 3G for this reason so assess carefully the expected lifespan of the technology you select alongside the deployment duration you are planning. By taking a long-term view of all the options you can engage with new IoT applications and upgraded hardware that delivers an operating model that opens up opportunities. You may not want to do things today that this platform can enable tomorrow. For example, a network that takes into account other options such as moving to a public cloud-based IoT platform to make it easier to access advanced 5G capabilities could have enormous long-term value.
Beyond the 2G and 3G sunset date
The sunset of 2G and 3G has not been an overnight, unexpected development and the cellular industry has created replacement technologies that offer good alternatives to common IoT connectivity needs. These take the form of 4G and 5G networks but also technologies that have been designed specifically for IoT devices. These technologies, narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) and LTE-M, were created to support the needs of IoT applications that are low cost, consume less data, have long battery lives and can operate in locations that are hard to reach, such as in remote areas or underground.
These capabilities will open up opportunities for new applications in agriculture, utilities, logistics and other industries. In addition, as 2G and 3G networks are being phased out globally, NB-IoT and LTE-M are the obvious replacements because they will soon offer global solutions when networks are fully rolled-out. LTE-M, in particular, is a good alternative for moving devices, such as fleet tracking and it can support voice technology.
LTE-M and NB-IoT will be the obvious choices for industries looking for 2G and 3G replacements for their devices with long lifecycles that require extended device battery life and coverage. Both technologies are good choices for deployments with expected lifespans of a decade or more, but there are differences between them which makes each of them more suitable for some IoT applications than for others. We believe the coverage of LTE-M and NB-IoT deployments may not, yet, be good enough everywhere, so we recommend enterprises verify coverage in more detail and/or ensure their devices are compatible with existing technologies as a backup.
IoT use cases will eventually move from old to new technology. As LTE-M meets or exceeds the technical characteristics of 2G/3G services, it appears to be a natural, evolutionary step. NB-IoT has lower responsiveness and limitations in mobility and may be relevant for use cases with lower data performance requirements but instead demands lowest possible power consumption and deepest indoor coverage.
Telenor IoT is working closely with our customers to support them during the transition to 4G/5G. We can help in planning the transition to ensure it is ready in time and in as cost-efficient way as possible, including working with partners to ensure access to needed hardware and expertise.
We also support our customers by helping evaluate opportunities for further modernization of the end-to-end solution and enable new functionality built on networks designed for IoT.
Determine what the transition means for you
We are committed to continuing to support our customers and partners throughout this entire technological shift.
If you’d like to learn more about Telenor’s 5G roadmap or want help determining what the transition from 2G and 3G to 4G and 5G means for you, get in touch.