What is 5G Technology and What Does 5G Mean for IoT?
An overview of 5G including a 5G definition, benefits and advantages of 5G, as well as opportunities for IoT.
Put simply, 5G delivers more data faster and more securely and this will be used to connect a new range of IoT devices and applications. The speed it offers has the potential to support new business models and change processes and business performance. However, today there are few use cases that need 5G capabilities and most IoT applications are well-supported by 4G or lower bandwidth network technologies.
What is 5G? - A Definition for this Mobile Technology
5G refers to the utilization of fifth-generation (5G) wireless technology. 5G is the next evolutionary step in mobile communications that has seen mobile networks previously mature from 2G to 3G to 4G. Away from the hype, what 5G really offers is low latency and high-speed connectivity.
For many IoT applications this will be a critical enabling technology but the bulk of IoT will continue to be well served by 4G and connectivity such as LTE-M, NB-IoT and Low Power Wide Area (LPWA) networks.
To explore the diverse array of IoT technologies and their transformative potential, including eSIM, LTE, 5G Redcap and more, visit our page about IoT Technology.
What Are the Benefits of 5G for IoT?
By connecting things enterprises can develop new or improve existing products, services, and business processes. From automotive to smart manufacturing and utilities, the role of IoT will grow in importance, transcending almost every industry. In addition, IoT will continue to benefit society by enabling implementation of government policy. For example, by enabling further control of electricity demand and fluctuating supply or minimizing waste of critical resources such as water. Today’s mobile networks, known as 2G, 3G and 4G, provide a strong foundation for connecting things. 2G, 3G and 4G were originally developed to enable personal communication and mobile broadband services. Still, they have also proven extremely capable for the demands of IoT, offering technical capabilities exceeding most existing use cases and with characteristics particularly well-suited to IoT.
For example, global standardization and coverage mean products and services can be scaled globally. Building on the scale of the mobile industry and billions of connected mobiles enables cost efficiency, reliability, security, and continuous development of devices, network technologies and service provider capabilities.
5G Key Advantages for IoT
- Enhanced mobile broadband
- Ultra-reliable low latency communications
- Much faster data in cities, urban areas and local networks
- Improved energy saving functions for devices used indoor
- Connectivity for the internet age in rural areas, because the aging 2G and 3G will be replaced with modern 5G
The Road to 5G from an IoT Application Perspective
5G Use Cases in IoT
5G is the first mobile network that has been designed from the ground up to support Internet of Things use cases (see 5G use cases for enterprises). When 5G was designed a number of use cases was considered, such as assisted driving, delivery robots, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), connected drones and public safety applications. The standard includes functionality to support a number of deployment scenarios, for instance:
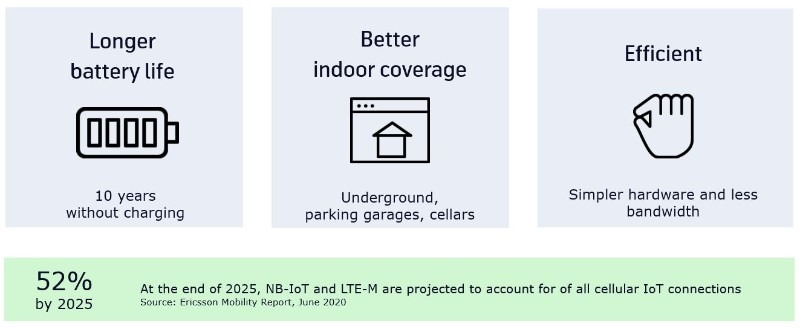
- Massive mobile IoT: Mass deployment for efficient and simpler IoT devices, for example sensors. These devices often send little data but cost, energy efficiency and reliable coverage can be critical for the use case to be relevant. 5G massive mobile IoT technology will enable low cost-devices with 10+ years of battery life and enhanced coverage even underground and in remote areas. Part of the technology to achieve this has been brought forward with 4G as NB-IoT and LTE-M and has in many countries been deployed before the 5G roll-out.
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband: 5G Enhanced brings more data. Today this is often used for data streaming. Enhanced Mobile Broadband is not only relevant for personal communication but also for IoT. Here the focus is on more data and throughput.
- Critical communication: 5G technology improves the predictability and security of data, providing a fast response which can be used in, for example, autonomous vehicles, or collaborative robots in Industry 4.0. Here the focus is on fast decision making by devices, using fast and predictable service characteristics.
How 5G Opens Up New Opportunities in IoT
5G is well-positioned to support IoT use cases that need continuous high-speed communication or rely on fast data analysis and decision making to deliver business benefits.
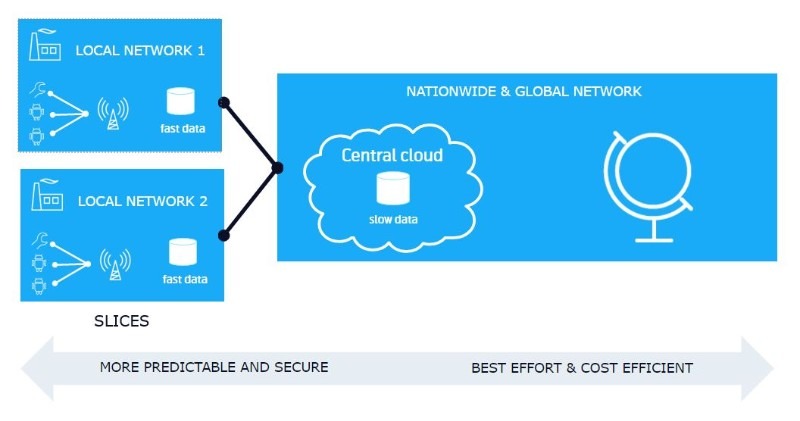
With 5G, IoT applications will also gain more control of the network characteristics and can program it to the needs of the use case. For example, with LTE-M and NB-IoT there is network functionality that allows enhanced coverage or reduced battery consumption for an application (see our guide on differences between LTE-M and NB-IoT). Over time it will be possible to take even more control over service levels, where data is processed etc.
Complementary technologies, such as network edge computing could take this even further, allowing the application to run in distributed cloud servers located close to the IoT device rather than in a centralized cloud data center.
Future Outlook for Mobile Technologies
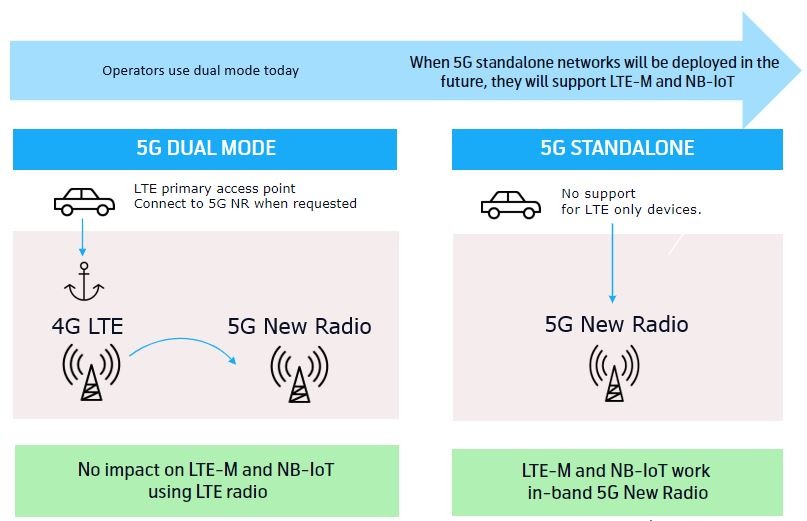
5G and 4G will both be available for the foreseeable future. 2G has been in commercial operation for more than 30 years and 4G/5G is likely to operate for at least as long. 5G has been architected from its initial design to co-exist with 4G technology. For enterprises this means that both 5G and 4G will be available for a long time. Mobile IoT and Dynamic Spectrum Sharing are two examples of this co-existence.
The Mobile IoT technologies LTE-M and NB-IoT were designed for 5G but rolled forward to work in 4G. LTE-M and NB-IoT were designed for efficiency for devices that use less data like sensors installed in buildings, and is suited for devices that have modest data requirements, but need a long battery life and comprehensive coverage.
Dynamic Spectrum Sharing enables Connectivity Service Providers to serve 4G and 5G devices on the same radio frequencies.
5G is currently mainly available in major cities in the developed world to offload 4G in crowded areas. In large parts of Europe, 5G, often in the form of LTE-M, will replace both 2G and 3G. We expect nationwide 5G and a replacement of 2G and 3G in many European countries to be a mainstream reality in 2025.
Also after 2025, we think that nationwide 4G technologies will continue to operate because 5G is designed to co-exist with 4G and 4G continues to be a very efficient technology.
Watch the Webinar about 5G for IoT
Join industry experts Martin Whitlock, CTO at Telenor IoT, and Jonas Karlsson, Product Owner at Telenor IoT, as they discuss the latest advancements and the future of 5G for IoT.