LTE-M Technology
An overview of LTE-M with LTE-M definition, drivers, adoption, use cases and deployment.
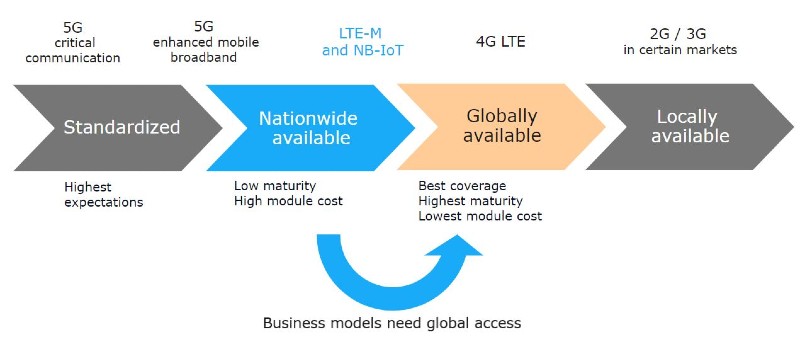
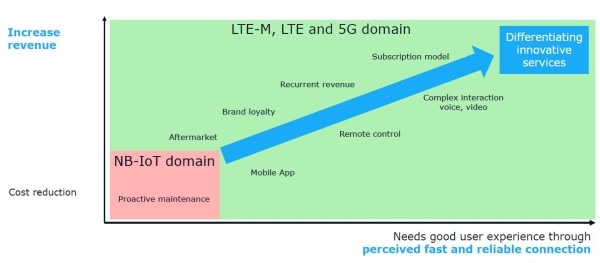
Why LTE-M Hits the Sweet Spot for 2G Replacement
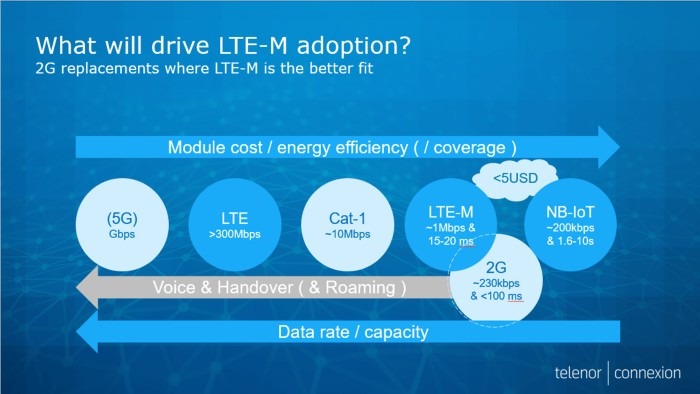
LTE-M is a simplified version of regular LTE which reduces hardware complexity and cost. Cost is not driven by number of components or complexity but by mass adoption and commoditization. The number of connected devices is initially low, which means that hardware module cost is relatively high at the moment but this will change as LTE-M IoT adoption increases. LTE-M is designed for roaming, just like 2G, 3G and 4G networks. LTE-M technology reuses all the roaming concepts that are found in regular LTE.
To investigate the extensive range of IoT technologies and their disruptive innovations, visit our comprehensive IoT Technology & Trends page. You can find in-depth insights about the shutdown of 2G and 3G in our white paper “2G and 3G sunset“.
LTE-M supports features that drastically reduce the power consumption of devices. This can result in a battery life of more than ten years. Battery life is extended by reducing the radio communication between device and network. New features of Power Saving Mode and Extended Discontinuous Reception allow for devices to deep sleep from up to several seconds up to several days. This comes with a cost of lower responsiveness, because a device that is sleeping and not listening is not reachable.
Drivers for LTE-M Adoption
Watch this Session from Telenor´s IoT Gathering 2023
In this session, The Latest Advancements in Connectivity Technology, Martin Whitlock, CTO of Telenor Connexion, shares Telenor IoT´s view on connectivity technologies such as LTE-M Cat1, 5G and 5G RedCap.
LTE-M Use Cases
There are numerous LTE-M use cases because it can handle more data through better bandwidth and lower latency. The agile software development methods used today, and increased security improvements will continue to drive the need software updates. This has a large impact on the bandwidth consumption during the lifecycle of devices.
LTE-M performs reliably deep inside buildings and remote locations, perfect for asset trackers, fleet tracking, alarm panels, pet trackers, health monitors, smart meters, and point-of-sale devices.
LTE-M is ideal for assets on the move because devices need to operate without a fixed power supply or regular recharging. And, due to the extensive coverage it provides, LTE-M allows you to track the location and status of assets, such as vehicles or containers, while maintaining a long battery life.
A variety of metrics are usually tracked, including fuel consumption, route, driver behaviour, etc. The condition of the goods can also be tracked by monitoring humidity, temperature, thereby enabling unforeseen problems to be rectified more quickly and avoiding spoilage.
LTE-M can support moving devices without losing data sessions at speeds of up to 200kmh.
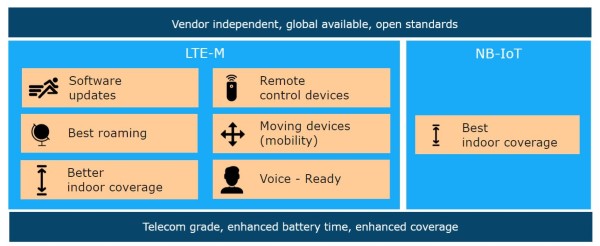
LTE-M is designed for voice because the specification includes Voice over LTE (VoLTE) which is deployed by 194 operators in 91 countries. However, VoLTE is not common in LTE-M yet. Not all networks are ready and VoLTE modules are not widely available for LTE-M, making them relatively expensive. We expect however that VoLTE will grow in importance in the coming years in LTE-M, just as it did in the consumer market for LTE.
Sony’s IoT Asset Tracking Solution Enabled by LTE-M Connectivity
LTE-M Strengths:
- LTE-M can handle firmware and software updates that are expected during the lifecycle of the devices.
- LTE-M can handle moving devices without losing ongoing data transfers.
- LTE-M has best support for international deployments on using a single point of contact and subscription for enterprises. LTE-M is built for roaming, like LTE.
- With LTE-M, devices can react in milliseconds if required, enabling use cases where a fast response is needed, relevant for the usability of human-machine interactions.
- LTE-M is prepared for voice technology and Voice over LTE.
LTE-M Deployment
LTE-M is widely available today on all continents.
GSMA maintains a mobile IoT deployment map. This includes Argentina, Australia, Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Finland, Germany, Japan, Mexico, The Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Romania, Singapore, Spain, Sri Lanka, South Korea, Sweden, Switzerland, Taiwan, Thailand, Turkey, United Arab Emirates and United States.
In Sweden LTE-M has been deployed recently and there are plans for LTE-M deployments in the United Kingdom for 2020.