Interactive guide to LTE-M vs NB-IoT
Our recommendation based on your answers
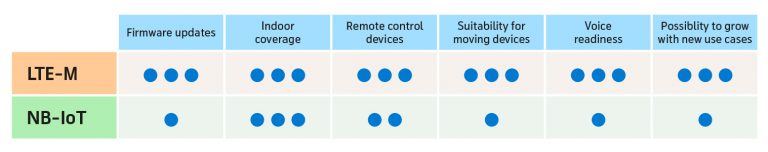
Based on your replies to the questions, LTE-M is the recommended choice. For most international IoT solutions we recommend LTE-M as the preferred connectivity standard as it is expected to become globally available faster and is more straightforward when developing and maintaining applications. LTE-M is built for roaming and has the best support for international deployments using a single point of contact and subscription for enterprises. It is also a better alternative for moving devices as it will not lose ongoing data transfers.
LTE-M operates on dedicated radio frequencies in telecom networks with a proven capability to scale, with committed support through the whole life cycle from the operator. It also supports improved battery life and substantial coverage enhancements, when compared to older mobile technologies.
Our recommendation based on your answers
Based on your replies to the questions, either LTE-M or NB-IoT are suitable connectivity technologies. They are both future proof, globally available, vendor independent technologies and based on open standards.
They operate on dedicated radio frequencies in telecom networks with a proven capability to scale, and with committed support through the whole life cycle from the operator. Both technologies also support improved battery life and substantial coverage enhancements, when compared to older mobile technologies.
NB-IoT may be the better choice in, for example, very large scale sensor networks where the requirements are known at deployment and the best possible indoor coverage is absolutely essential.
However, for most international IoT solutions we recommend LTE-M as the preferred connectivity standard as it is expected to become globally available faster and is more straightforward when developing and maintaining applications. LTE-M is built for roaming and has the best support for international deployments using a single point of contact and subscription for enterprises. It is also a better alternative for moving devices as it will not lose ongoing data transfers.

Recommended readings
Unsure what the difference is between eSIM and eUICC? Where can it be used? And are there any benefits? Download our white paper to answer these questions and more about the technology.
Read moreRecently we held a webinar on LTE-M vs NB-IoT. This was followed by a number of questions which we share here.
Read more