Explore the benefits of IoT in smart manufacturing and connected machinery, and learn how Telenor Connexion works with industrial machine manufacturers to integrate IoT technologies.
Smart manufacturing defines an environment in which computers are in charge of decision-making. In a smart manufacturing environment, physical and digital are connected and communicate with one another to improve production.
Industry 4.0 is a name given to the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. It includes cyber-physical systems, the Internet of things, cloud computing and cognitive computing. (see also IoT for manufacturing)
Connected machines used in factories, refineries and all manner of industrial environments provide the tools to streamline operations, optimise productivity and improve ROI.
One of the keys to success in Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing is adding IoT connectivity to machinery. Read our white paper to find out how.
The opportunities and challenges presented by Industry 4.0 for industries like manufacturing, energy, gas and oil, and construction are many and varied. Before adopting IoT, it’s important that enterprises understand the underlying opportunities and key challenges that exist.
In the industrial sector, IoT adoption can result in greater optimization of business workflows and processes, enhanced safety, improved research and development, and the creation of new revenue streams.
Telenor Connexion is dedicated to helping its customers identify the business value of connectivity and showcasing how IoT can be used by enterprises to create solutions that solve problems and unlock new revenue streams.
For industrial machine manufacturers, that means reduced machine downtime, increased safety, increased quality control, a data-driven supply chain, improved inventory, and much more.
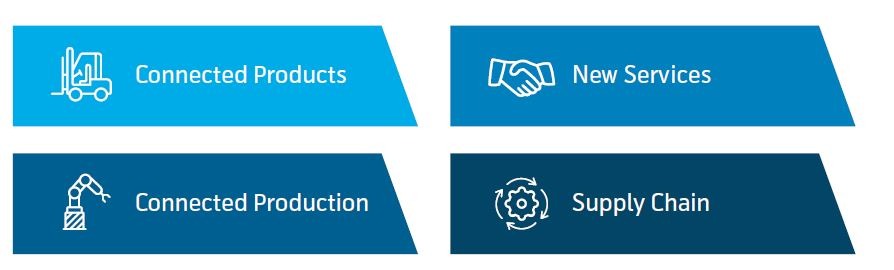
Digital transformation in manufacturing: manufacturers are focused on digitalization in four areas – connected products, connected production, new services and supply chain
IoT-enabled manufacturing provides full visibility of assets, processes, resources, and products. This, in turn, supports streamlined business operations, optimised productivity and improved ROI.
The key to success is connecting equipment, integrating diverse industrial data, and securing industrial systems for the entire lifespan of equipment.
Connectivity allows a manufacturer to not only improve and automate production, but expand their offerings with services that connect directly with customers.

With connectivity, machine performance can be optimized through its entire lifecycle with over-the-air (OTA) firmware. This increases efficiency and reduces costs for the manufacturer. Two-way data communication also allows the machine manufacturer to collect data for R&D. This data can be used to identify emerging trends about user behaviour, to refine existing services and eventually create new ones.
Machine service processes can be streamlined with a smart product. If a problem occurs, the machine can send an alarm to the owner/operator and service providers.
With a connected offering, the manufacturer can tighten the bonds with their dealer and service ecosystem. This makes the manufacturer more appealing to work with, while providing a more consistent customer experience.
Choosing the right connectivity technology is one of the critical decisions that a manufacturer needs to make when designing connected products.
Though production machinery might be static and installed indoors, mobile connectivity is still the right choice for many manufacturers. Using a mobile SIM card-based solution allows the manufacturer to avoid the problems of connecting to the end-customer’s local network using Wi-Fi or other radio technologies.
No matter where the machine is first deployed (or where it ends up) mobile networks offer a highly-available and reliable source of connectivity. With quality of service guaranteed by service level agreements (SLAs) from the connectivity provider, a manufacturer can confidently offer their customers services such as secured product uptime.
When we ask manufacturers what they need from their IoT solution, fast deployment, global scalability and rapid return-on-investment are always high on the list. Telenor Connexion have a long history of working with manufacturers to achieve these goals.
The data that your connected products generate must be easy to turn into business value. You need tools to make data easy to understand and easy to integrate into your business processes. Our Managed IoT Cloud provides flexible and intuitive data-visualization tools that will allow you to get started in days rather than months.
Value-adding offerings tied to a connected product can evolve through its entire lifecycle.
Succeeding with servitization requires reliable connectivity and easy access to data analytics. Working with Telenor Connexion allows you to focus on your products and user experience while we provide the supporting infrastructure.
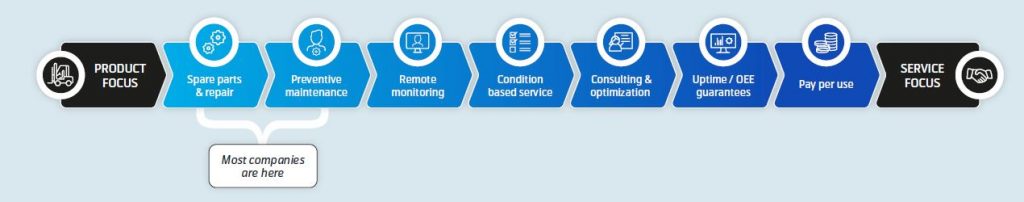
Differentiating your product from the competition can be difficult. Once connected, your products can eventually become the touchpoint for evolved services that are integrated in your customer’s operations.
For example, in the future a company that manufactures forklifts may decide to not only sell their product to the customer via a dealer. Instead, they may offer a package of operating hours, selling the machine’s capability “as a add-on service” – not necessarily the forklift itself. This could involve a range of add-on services such as data on user behaviour, consumables, machine performance and many other metrics. This is an opportunity that often develops over time. However, most manufacturers start more simply, by connecting a product where the benefits are clear.
With a Product-as-a-Service offering, the value provided by the manufacturer is reliable, on-demand performance.
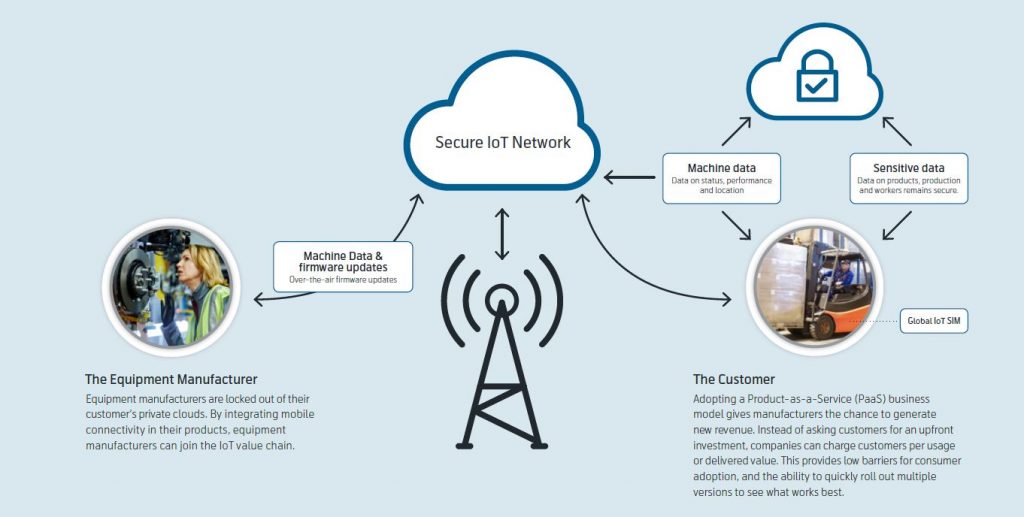
IoT enables manufacturers to make the shift to more responsive, adaptive and connected manufacturing.
As a result, the smart factory is a fully connected and flexible system that can adapt efficiently to the demands of a changing marketplace.
As sensors and IoT solutions become more accessible and affordable, production inside the factory becomes more connected. But the data from production equipment and machinery is often locked inside the smart factory.
In order to join the IoT value chain, the businesses that build and supply manufacturing and processing equipment need access to the data from their machines. But closed networks are a barrier to achieving all of the benefits of digitalization and IoT.
Connected things inside the smart facility can talk to each other, but manufacturers are sometimes reluctant to connect their factories to the cloud.
Equipment manufacturers are often locked out of the private cloud inside the customer’s factory. Mobile IoT connectivity provides a plug-and-play solution to that obstacle. IoT can help ensure sensitive data, such as process results, remains secured within the factory, while non-sensitive data can be made available outside it. This connected production process is responsive and adaptive, thereby freeing customers up to focus on their business and services.
Connectivity in logistics is not new, but thanks to the proliferation of sensors along the value chain, connectivity is expanding from ‘high-value’ assets to mass deployment.
A connected supply chain enables optimization and savings through the value chain – for the manufacturer, service provider and end customer. Manufacturers can leverage the connected supply chain to move to just-in-time production, whereby materials, goods, and labour are scheduled to arrive or be replenished exactly when needed in the production process. This allows the manufacturer to avoid costly overstock and move to demand-based production. For the customer and service provider, optimizing parts purchasing, inventory and replacement is easier when connected machines report what they need and when they need it. This way, the service provider can improve customer satisfaction and the customer can avoid downtime.
Please feel free to read more insights on IoT for Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing.