Key AIoT Benefits: Exploring Dynamic AI & IoT Use Cases
Explore the primary benefits of AIoT, such as increased productivity gains, along with real-world use cases across various industries.
The Benefits of IoT With AI
AIoT is of strategic importance for global IoT enterprises, it is an operational necessity for businesses aiming to fortify their relevance and resilience in the digital age.
The marriage of AI and IoT is not an incremental upgrade but rather holds the key to unlocking higher operational efficiencies, better customer experience, and higher productivity gains across diverse sectors from automotive and industrial manufacturing to supply chain, transport & logistics, utilities, and smart cities.
This article is an excerpt from the Telenor IoT Predictions Report, produced in cooperation with Omdia. Find out more about AIoT strategies for enterprises or download the entire report for free below!
IoT Predictions 2024: AIoT to Emerge as the Defining Enabler of Digital Transformation
In these and other applications, this convergence can turn simple solutions into those with greater impact and value. Predictive maintenance, robotics improvement, and enhanced in-car experiences underscore the tangible ROI of the Artificial Intelligence of Things.
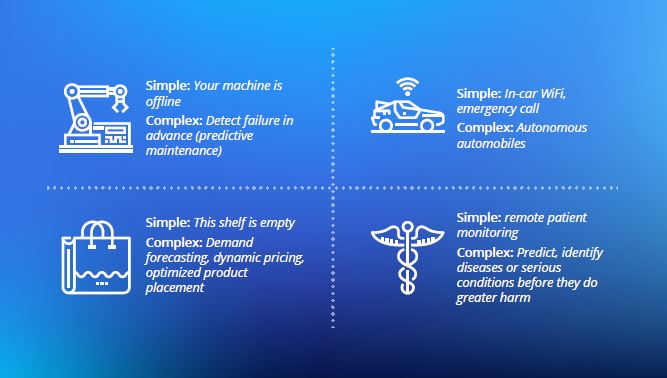
AI and IoT Use Cases in Key Sectors
AIoT in Manufacturing
By adding IoT to a factory setting, manufacturers can access real-time monitoring of various factory assets. Deployment of most modern AI/ML technologies can take this to another level, allowing these solutions to identify anomalies and in turn predict equipment failures before they cause downtime. The ROI of predictive maintenance is evident. If trained on high-quality data, not only can AI systems trigger appropriate actions to be taken automatically to prevent component failure and replacement, but also ensure that manual inspections are only done when needed. Thus, allowing for reduced equipment and personnel expenses.
The ability of the Artificial Intelligence of Things to improve robotics is also important for the manufacturing industry. Already, Tier 1 manufacturers are pushing hard for autonomous factories and warehouses where robots and Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are integrated for identification, retrieval, and smart palletization – for example, DHL expanding their partnership with AutoStore for 1,000 automated warehouse robots. The trajectory of collaborative systems will likely be accelerated by the more advanced capabilities of AI, connectivity and guidance systems such as Robot Operating System (ROS). Communication between these robots and humans will also be improved using natural language processing (NLP) technologies.
AI in Automotive
Over a fifth of all vehicles in circulation are already connected, and this is anticipated to reach 100% by 2030 –with each individual vehicle generating huge amounts of data from a vast array of sensors in multiple applications and functions. The next logical step is to embed AI/ML within these vehicles to help use this data to deliver safer driving experience, improved vehicle performance, and enriched customer experiences.
Already AIoT is playing a role in the in-car experience through voice assistance. Using the new generation mobile and IoT connectivity and the power of AI, these systems interpret driver cues and speech and convert those into recommendations for action. The functionality and reliability of these systems continue to grow as advancements are made in NLP. Artificial Intelligence is also contributing to driver-assist safety systems seen on many vehicle models such as blind spot monitoring which warns drivers when potential obstacles are nearby.
Looking ahead, AIoT will play a central role in reaching the goal of fully autonomous cars. These vehicles will require continuous, uninterrupted streams of data through IoT connectivity and advanced AI models that can immediately and accurately identify, label and respond with action to vehicles, people and objects on the road. These solutions will be complex, requiring an enormous amount of training on a wide range of datasets so that every scenario can be processed and acted on in split-seconds. While the challenges are tremendous, so too are the benefits as most studies estimate over 90% of serious automotive accidents are due to human error. As a result, Omdia believes autonomous driving could represent one of the most impactful AIoT solutions in the years to come.
Zenseact and the Autonomous Vehicle Drive
Zenseact is an AI software company known for its OnePilot product, founded and since fully acquired by Volvo Cars in 2023– a clear sign of the increasing importance of embedded AI within automotive as the industry moves from connected car to smart vehicle. Zenseact are even working with CERN, one of the world’s largest and most respected centres for scientific research, in exploring deep learning models and computer vision techniques to help improve decision-making in autonomous vehicles, with faster algorithms and more energy-efficient models for delivery at the edge.
OnePilot is an AI-powered software platform for autonomous driving and advanced driver-assistance system (ADAS) applications. This platform is already at work in Volvo and Polestar vehicles, with the first production launch on the Polestar 3 in October 2022. The focus is on advanced driver assistance, using AI methods to power active safety capabilities, termed ‘precautionary safety’ by Zenseact– allowing the vehicle to be able to anticipate dangerous traffic scenarios before they happen and adjust the car’s speed and position accordingly. For example, this includes the use of high-definition maps to allow the vehicle to understand positioning and stay in the centre of lanes, even when markings are difficult to identify. Real-life data from the vehicle fleet is also then used to build ‘collective fleet intelligence’ to aid continuous improvement of the solution.
All of this of course requires strong and reliable connectivity, especially since the vehicle will continuously improve its performance and functionality through over-the-air software updates.
IoT Use Cases
AI in Smart Cities
AIoT also becomes a key enabler for sustainable smart cities, as enterprises and governments across the globe work towards the sustainable development goals (SDGs) set by the United Nations in 2015 and focus on the transformation within cities. IoT is among the fundamental technologies here, where sensors and devices collect all the necessary data and information that allow city planners to monitor their progress against sustainability KPIs, such as improving energy efficiency, reduce pollution, optimize traffic networks and similar.
As the number of sensors and generated data increase within city environments, AI and ML are important for automating processes and creating more value from this data. For example, AIoT solutions can combine historical and real-time traffic data to predict and in turn alleviate congestion areas. Similar to the predictive maintenance in manufacturing, AI can enable more accurate predictions of potential downtimes/failures in city services (such as waste management and water supply) and risks such as natural disasters.
Telenor and Ericsson Aim to Improve Energy Efficiency in Telecoms
In November 2023, Telenor and Ericsson announced the signature of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) focused on the aim of advancing the realm of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies within the telecommunications industry, but particularly towards enhancing energy efficiency without compromising on connectivity quality. The partnership is based on the clear trend towards more programmable mobile networks, such as through AI-enabled decision and operational support.
Ieva Martinkenaite, Senior Vice President & Head of Telenor Research & Innovation, said, “AI adoption is essential for Telenor to unlock our customers’ potential. We expect this collaboration to break new ground when it comes to leveraging AI and automation to help address the complexity of 5G networks, drive energy efficiencies, improve customer experience – and make Telenor an AI-first company.”
The partnership focuses on two key areas of engagement:
- Energy Management and Network Optimization: Telenor and Ericsson will work together to develop and implement AI-driven solutions to optimize energy consumption and enhance network performance, particularly in radio access networks (RAN).
- Implementation of Safe and Trustworthy AI: The partnership will also emphasize the development of explainable AI systems to ensure transparency and reliability in network operations.
The collaboration also outlines four key areas of expected outcomes, including:
- Research Insights: Joint publications on advanced ML methods in mobile networks, covering topics such as energy optimization in RAN and secure, explainable AI.
- Live Test Network Deployment: Testing and deployment of AI/ML systems in a live test network, including energy efficiency, anomaly detection, and spectrum sharing, in cooperation with early adopters and Telenor customers.
- Validation of Business Models: The validation of AI-driven 5G use cases and business models.
- Knowledge Building: Creation of teaching modules and similar resources to accelerate growth potential in AI-native telecommunications.