Leveraging AIoT: Essential Strategies for Enterprises
Explore key 2024 strategies for effectively adapting to the evolving technological landscape, seizing transformative advantages of AIoT, and ensuring success in the digital age.
In an era marked by the rapid evolution of digital transformation, the need for enterprises to access timely, high-quality data and process such data sustainably is at the forefront of strategic considerations. This necessity extends to the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT), and the acquisition of new, unique sources of data in the form of real-time information from interconnected sensors and devices. This plays a pivotal role for fundamentally new ways of creating value across industries by combining digital and physical worlds.
The significance of an IoT solution transcends mere data collection, requiring processing and augmentation capabilities of modern Artificial Intelligence (AI) to achieve true impact. The combination of AI and IoT, often termed the Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT), further enabled by new generation connectivity such as 5G, represents more than an incremental enhancement. This convergence unlocks higher operational efficiencies, better customer experience, and higher productivity gains across diverse sectors, from automotive and industrial manufacturing to transport, utilities, and smart cities.
This article is an excerpt from the Telenor IoT Predictions Report, produced in cooperation with Omdia. You can download the entire report for free below!
IoT Predictions 2024: AIoT to Emerge as the Defining Enabler of Digital Transformation
Now Is the Time to Act
The transformative nature of IoT with AI is acknowledged, marking a shift from ‘smart’ connected products to a seismic advancement in the market. The time to act is now for organizations aspiring to compete in the digital age or they will fall behind.
As the saying goes “Nothing great ever came that easy”. It is not a surprise given the impact of these solutions that they also are complex to adopt.
Amongst many factors, as enterprises begin their AIoT journey, they should certainly consider the following:
- Set digital transformation ambitions and translate those to tangible and measurable business goals (and adjust them if needed) – While urgency to move forward with the Internet of Intelligent Things is needed, don’t start your adoption unless your AIoT initiative is either solving a business problem or creating a genuine business opportunity. Furthermore, ensure you have mechanisms in place to measure the success of that project. Also, expect those KPIs to evolve. Given their infancy, KPIs for less mature AIoT use cases will evolve rapidly.
- Enable experimental, learning culture with an appetite for higher risk – Implementing AI within organizations is not a simple hardware or software implementation; it requires a fundamental mindset shift and new leadership on how we do things in an organization. One element of this is to enable an experimental culture allowing people to break things fast with calculated risks and shared accountability, learn from mistakes, and ensure continuous skills development. This also requires broader, longer-term thinking about the AI4IoT lifecycle, particularly ongoing tuning and maintenance and the important role of data integration and governance.
- Take a practical approach to managing Responsible AI risks – The power of Artificial Intelligence is immense but when used improperly it creates exposure to risks that include regulatory penalties, litigation, loss of revenue, and loss of customer/partner confidence. Building trustworthy AI outcomes is no trivial matter, demanding effort and expertise across a wide range of disciplines, including privacy, security, transparency, bias, and safety. For AI to flourish, Omdia believes enterprise AI practitioners must practice Responsible AI and address issues of ethics and governance by establishing a set of transparent, measurable, and enforceable ethical standards, taking the opportunity to upskill teams and deliver better outcomes.
- Work with the right partners – Artificial Intelligence experts are scarce resources and will remain so in the upcoming years. As a result, for many enterprises working with AI technology partners is critical to completing their AIoT journey. These partners may help the users remove roadblocks, do joint upskilling, deliver projects on time, and achieve ROI targets.
As with any transformative technology, the ultimate impact of AIoT is hard to gauge. However, Omdia does believe that 2024 marks a significant fork in the road, a point in which the Internet of Intelligent Things will go from optional to a requirement for any organization with ambitions of competing in the digital age.
Cellular Connectivity Will Allow AIoT to Flourish
The transformational power of AIoT is clear – and one essential element to allow these applications to improve over time and solve new business problems is connectivity. Full-scale, deployments of IoT Machine Learning simply will not be impactful unless they have access to reliable and ubiquitous communication networks. Connectivity is the lynchpin bringing it all together.
The importance of connectivity for the growth of AIoT, comes down to one word: data. The incredible amount of data provided via the IoT is an essential fuel driving AI/ML algorithms to improve the accuracy and speed of decisions. Quite simply, the more data and more high-quality data these AI systems have access to, the more capable and powerful tools they can be for enterprises.
The combination of IoT connectivity and AI essentially creates a mutually beneficial loop. Of course, if the transmission of this data is limited, inconsistent, or never occurs then this loop cannot be completed.
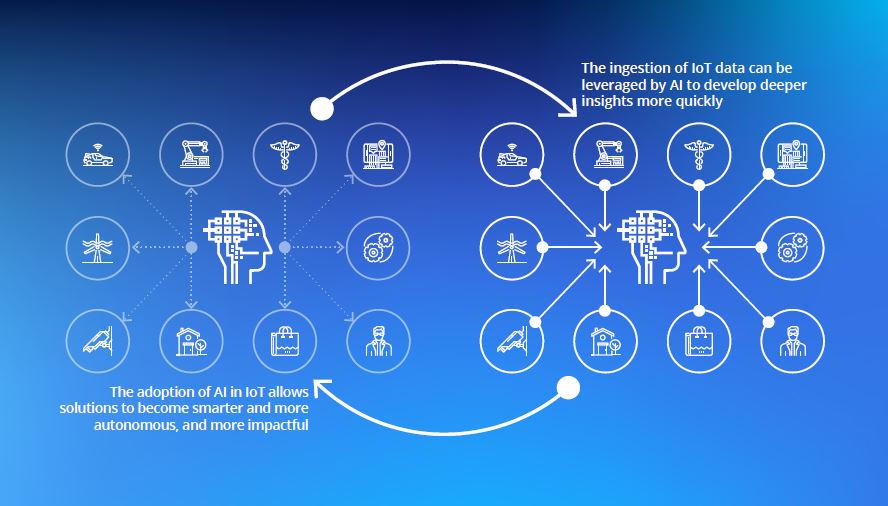
Today, enterprises have various short-range, long-range, wired, and wireless connectivity protocols they can use in their AIoT deployments. In many instances, cellular connectivity has advantages; including the technology’s proven scalability, and its inherent security thanks to encryption and well‑established protections. Additionally, a unique challenge related to AIoT is the diversity of devices and environments. Each can present different requirements and necessitates a service provider that can support multiple connectivity standards. Here again, cellular technology shines as its diverse protocols can meet these various demands.
For instance, many IoT devices are deployed in the field, often in remote locations. This presents a tremendous challenge in terms of network coverage, but also often correlates to these devices having limited access to power sources. Energy efficiency is required. In these instances, the availability of low-power wireless cellular networks, such as LTE-M or NB IoT, is essential.
At the other end of the spectrum are IoT applications that require high speed and low latency. In this scenario, advanced network standards such as 5G are required to provide high-bandwidth connectivity. Finally, even in cases of Edge AI where the need for ubiquitous connectivity is certainly lessened, a network is still vital to ensure firmware updates, and updates to the AI model itself, can be communicated.
No single connectivity technology is suitable for all IoT applications. Many IoT projects use multiple protocols. A partner with years of experience can help an enterprise choose the most suitable technology (based on cost, coverage reach, power consumption, etc.) for a specific project. This partner can also assist in interoperability testing when multiple protocols are being used together.
Telenor´s IoT Offering
About Telenor IoT
Get a Free Consultation