IoT Technology & Trends
All around us, the pace of change is accelerating. Explore how industries are adapting and learn about the IoT technologies leading the way, now and into the future.
What Is IoT Technology?
IoT Technology definition
IoT, or Internet of Things, refers to the network of interconnected physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and other objects embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity capabilities. These devices can collect and exchange data over the internet without requiring human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction.
IoT technology enables these devices to communicate and interact with each other, gather and transmit data, and perform various tasks autonomously or with minimal human intervention. It involves a combination of hardware, software, connectivity protocols, and data analytics to create a seamless ecosystem where devices can connect, communicate, and collaborate.
In 1999, Kevin Ashton coined the term “Internet of Things” (IoT), envisioning a world where everyday objects connected to the internet through tiny sensors. Some of the earliest IoT projects included monitoring inventory in vending machines and real-time tracking of oil pipelines. These pioneering efforts marked the start of a profound transformation, where IoT now encompasses interconnected devices in homes and industries, driven by Kevin Ashton’s visionary idea from 1999.
The Internet of Things is transforming many industries and creating value for both businesses and their customers as one of the key enablers of digital transformation. Deploying IoT entails securing an end-to-end technology stack that includes device hardware (such as connectivity module, sensors, processor) that are embedded in the connected “thing”, connectivity technology that determines how the device will connect to the internet and transfer data, cloud platform where data is captured, processes and stored and applications (software) for data analytics, machine learning, device management and various business applications.
IoT Technology Stack
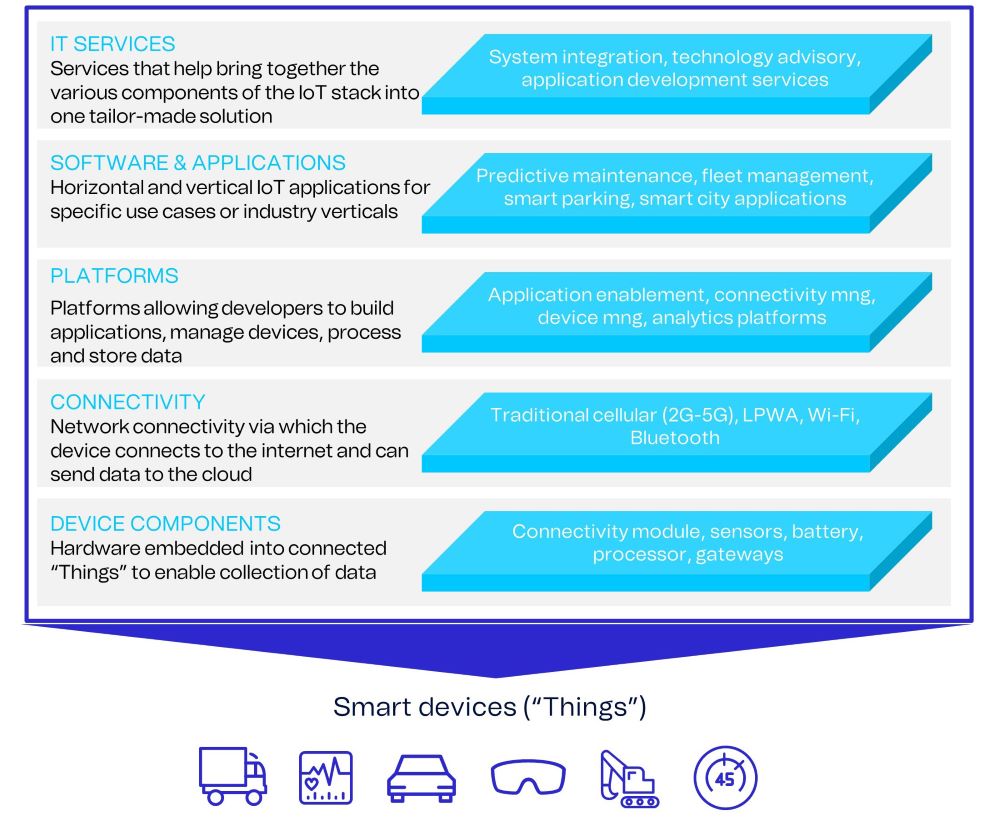
The key elements of IoT technology include:
1. Devices and Sensors: IoT devices are equipped with sensors to collect data from the surrounding environment. These sensors can include temperature sensors, motion sensors, GPS modules, cameras, and more.
2. Connectivity: IoT devices use various connectivity options, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular networks, and Low-Power Wide-Area Networks (LPWANs), to establish communication and transmit data.
3. Data Communication: IoT devices send and receive data over the internet, often using cloud-based platforms or edge computing systems for data storage and processing.
4. Data Analytics: IoT technology involves analyzing the collected data to extract meaningful insights, identify patterns, and make data-driven decisions. This can involve applying machine learning algorithms, predictive analytics, and artificial intelligence techniques.
5. Applications and Services: IoT technology enables the development of various applications and services that leverage the collected data and enable automation, efficiency, and new business opportunities across industries.
Overall, IoT technology is revolutionizing the way we interact with the physical world by connecting everyday objects and enabling them to communicate and collaborate, leading to improved efficiency, enhanced productivity, and new possibilities for innovation.
Deployment
Deploying IoT entails securing an end-to-end technology solution that includes hardware (device, components), connectivity technology, and platform and applications (software), which are often brought together with the help of a system integrator or technology consultancy.
Advantages
Each of these IoT technologies is important and carries its own requirements. IoT technology enables organizations to realize efficiencies and capture opportunities and therefore brings together horizontal technology such as connectivity and cloud computing with vertical technology such as industry-specific software and applications plus sector-focused devices.
Watch the Session "The Latest Advancements in Connectivity Technology" from Telenor´s IoT Gathering 2023
As mentioned in the video, the 2G/3G sunset and 5G RedCap are important topics impacting the future of connected devices.
Key IoT Technologies
To harness the full potential of IoT, a range of technologies work in tandem. These technologies include:
– Cloud Compute Resources: Leveraging cloud infrastructure for data storage, computing power, and scalable resources.
– Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC): Moving computation closer to the network edge for reduced latency and improved real-time processing.
– Machine Learning: Employing algorithms and models to enable devices to learn from data and make intelligent decisions.
– Artificial Intelligence: Utilizing AI techniques to enable devices to simulate human intelligence and perform tasks autonomously.
– Data Analytics and Processing: Extracting valuable insights from collected data through analysis and processing techniques.
– Security: Implementing robust security measures to protect IoT devices, networks, and data from unauthorized access.
– Over-the-Air (OTA) Upgrade: Enabling remote software updates and upgrades to IoT devices for improved functionality and security.
– Device Management Software: Facilitating device provisioning, configuration, monitoring, and maintenance throughout their lifecycle.
In addition to these IoT technologies, IoT also relies on well-established enterprises systems. To explain IoT enabling technologies requires an understanding of the end-to-end business process that IoT capabilities are enabling and which adjacent technologies and software are required will depend on the individual service or application. Frequently used systems include enterprise resource management, product lifecycle management, billing and charging, sales tools, CRM and CX-related software and cloud management systems. This is not an exhaustive list and often the benefits of IoT technology are unlocked by applying machine learning and artificial intelligence to IoT data in order to enable greater automation and operational business cases.
Scalability and Provisioning
IoT is all about doing things at great scale. To ensure successful deployments, IoT technologies must handle growth into hundreds of thousands or even millions of connections. Configuration, provisioning, security, and upgrades need to be provided with minimal human interaction to enhance profitability and time-to-market.
Conclusion
Choosing the right IoT technology is crucial not only for the early phase of deployment but also for the long-term vision of IoT reaching a mature stage of massive scale. Taking the time and care to make informed technology decisions will ensure alignment with this vision. Our report “Connectivity Technologies” will give you more detailed information.
IoT Basics - A Guide to IoT Terminology
This guide helps you understand the Internet of Things and connected devices. We explain over 185 IoT terms and technologies.